
Free Download Altair EDEM Professional 2023.0 | 1.1 Gb
Owner:Altair
Product Name:EDEM
Version:2023.0 Professional
Supported Architectures:x64
Website Home Page :www.altairhyperworks.com
Languages Supported:english
System Requirements:Windows *
Size:1.1 Gb
Altair, a global technology company providing solutions in product development, high-performance computing and data analytics, is pleased to announce the availability ofAltair EDEM Professional 2023.0, the market leading Discrete Element Method (DEM) software for bulk and granular material simulation.
Altair EDEM Professional 2023.0 Release Notes
Here are some more details of the key highlights from this latest release!
Combining multi-sphere, polyhedral and sphero-cylindrical particles
One of the main additions in this release is that it is now possible to add Sphero-cylinder, Multi-Sphere and Polyhedral particles to the same simulation. Since the addition of polyhedral and sphero-cylinder particle shapes to EDEM, users have been requesting to combine all shapes in the same simulation to further enhance their results. Now, any particle shape currently supported can be combined in a single simulation with any other particle shape, providing users with deeper insight and analysis for all industry applications. This offers users the ultimate flexibility with mixed particle shape simulations where users can mix and match particles like never before!

In addition, the mixed particle shapes are supported for the materials database, meta-particle, volume packing, material block functions, and particle attributes has now standardized outputs, such us diameter and length.
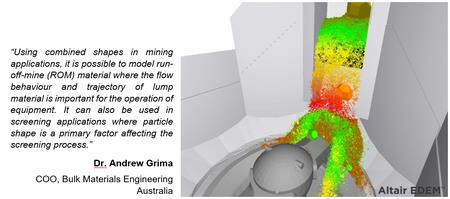
High Performance Bond Model for all Particle Shapes
A new bond model has been added – the Linear Elastic Bonding Model (LEBM). Previously, users has been restricted to the traditional Bonding V2 model designed for spherical particles. With the addition of polyhedral and sphero-cylinder particle shapes, an alternative model was required to cater for more complex scenarios for specific types of applications. This new model forms elastic bonds between particles that can be broken under tensile or shear forces, allowing better performance and removing the need of a base model, like Hertz-Mindlin.
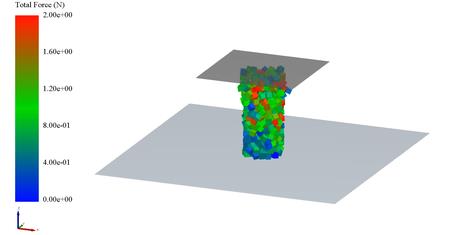
New Residence Time Analysis
New residence time analysis for defined regions is now available to allow users to track the time a particle has spent in a region. Some applications require this type of analysis in a specific region in the equipment, while the current residence time (EDEM 2022.3 and lower) only allows users to consider the full domain. The new analysis also uses different container shapes like spherical or cuboids and offers more insights into particle behavior and particle tracking with better precision.
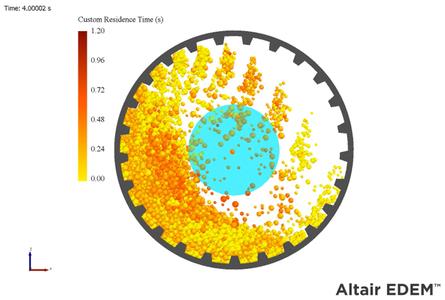
New Fully Integrated API GUI for Custom Models
EDEM’s API has been revolutionized with the ability to create user-friendly interfaces for custom models, eliminating the use of old text-based preference files. Using the old text-based preference files, the values entered were not saved in the simulation files. Now, the models are fully integrated and behave like a built-in model without losing data and performance.
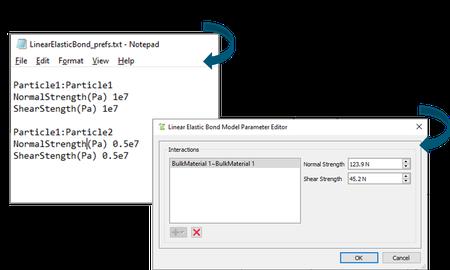
Users also benefit from a more user-friendly interface that also allows more complex physics for the contact model API. All API models can now easily be configured and maintained by customizing them as required at any time using tabulated parameters.
What else?
EDEM 2023 includes several other additions and improvements in the GUI and performance increase in the solver for multi-sphere and polyhedral shapes. EDEMpy has also been updated to include new capabilities, like volume packing, particle size distribution setup or parallel processing.
EDEM 2023 contains fixes for the following issues:
– The cell size was editable after running a simulation using the CUDA solver.
– A crash when running the CUDA device test has been fixed.
– The method used for random orientations had a tendency to bias specific directions. A new method has been implemented which addresses this bias and gives a better ‘random’ orientation.
– The STL export would crash when exporting time steps with particle types which have no particles.
– The filename could not be manually defined for the stl export. A filename can now be entered directly into the output file text box in the Export to STL dialog, if no full path is entered the export file is saved relative to the current deck.
– Errors could occur when changing the deck from a polyhedral deck run on CUDA to a multi-sphere deck run on CPU.
– The transfer material could not be used due to an error message which could not be dismissed.
– Two contacts were generated when a particle touched the line between two geometry elements.
– An error message could appear when using Polyhedral Particle and material blocks.
– Additional parameters were stored in the data files for the Edinburgh Elasto Plastic Adhesion model.
– Gravity was added after the setTotalForce was used on CUDA. CUDA plugin API body force models will now work with the total particle force, including gravity. This means that calling NCudaApiTypesV1_0_0::CApiTotalForce::getTotalForce and NCudaApiTypesV1_0_0::CApiTotalForce::setTotalForce will return or set values including the gravity force acting on the particle. This now matches the CPU API behavior.
– Overlapping Sphero-Cylinder particles could be removed from the simulation rather than resolving the contact if the end points were exactly coincident.
– Exporting geometries to .stl could cause excessive memory usage.
– The time was not updated in the Coupling’s setEDEMTime() function when the EDEM Solver was active.
– Sphero-Cylinder particles could report NaN values for the velocity in extreme situations.
– Deleting a single particle in Creator deleted all contacts from the timestep, rather than just the contacts for that particle.
– A potential issue with the polyhedral spinning friction model which would occur when the model was used alongside cohesive models has been fixed. Previously it was possible for a nonphysical amount of tangential ‘rocking’ damping to be calculated in this case, but now for attractive forces this damping will not be added. Note that the ‘rocking’ damping corresponds to relative angular velocity perpendicular to the contact normal while the ‘spinning’ damping corresponds to relative angular velocity parallel to the contact normal and the ‘spinning’ component has not been changed.
– EDEM could hang if a coupling application was disconnected mid-simulation.
– EDEM could crash rather than report an error in some cases when using the CUDA solver and custom properties.
– Opening deck as read-only with EDEMpy changed the ‘time modified’ of last timestep. No h5 files should be modified now unless the deck is opened in read write mode.
– CUDA rolling friction Type C model was using the contact overlap instead of physical overlap to compute the Kn.
– The path for PM FlexTire was not checking that the path to the file was correct before starting the simulation.
– EDEM did not report a clear message when invalid video settings were used on Linux.
– It was possible for particles contacting with zero angular velocity to receive undefined torques and then disappear from the simulation when using the RVD rolling friction model in the CUDA solver.
– A crash could occur when exporting data during the simulation.
– Continuum Planes and Plane Groups could not be deleted from a simulation.
– The density sensor would show the wrong value when the units were changed.
– The PSD graphs could show the wrong values when the particle was modified during the simulation.
– Display of Cylindrical Periodic Boundary Conditions was not independent between the Creator and Simulator views, and settings were not retained when the file was saved.
– The thermal conductivity edit box in the Heat Conduction contact model parameter editor would be resized vertically along with the editor. This was also true for other edit boxes in other parameter editors.
– A memory leak could occur when adding custom properties in API contact models.
– When saving a blank file or using the ‘Save as’ option, the viewer display would disappear temporarily until the user clicked somewhere on the screen.
– The results for Breakage were not repeatable on the same device. The ability to have a random seed has been added to the breakage model for random start (with repeatability off).
– Simulations which had geometries changed from physical to virtual could crash when starting with the CUDA solver.
– Simulator would fail to unlock Simulator Queries files when stopping.
– The options given by the warning message which occurred unchecking the face of a box geometry with a factory did not give the correct behavior.
– Changes to density value in creator with auto calculation enabled would recalculate particle properties for all materials, rather than just those for the changed material.
– A crash could occur when using particle templates when the template used was not found.
– The solve report did not give the correct information if the simulation was not saves and re-loaded before running.
– The IParticleManagerApi_1_5 could not be used in configForTimestep functions in v3.6.0 plugins
– The edempy deleteKinematic method did not work.
EDEMis high-performance software for bulk and granular material simulation. Powered by state-of-the-art Discrete Element Modeling (DEM) technology, EDEM quickly and accurately simulates and analyzes the behavior of granular materials such as coal, mined ores, soils, fibers, grains, tablets, and powders. EDEM simulation provides engineers with crucial insight into how those materials will interact with their equipment during a range of operation and process conditions. EDEM is used for virtual testing of equipment that handles or processes bulk materials in the mining, equipment manufacturing and process industries. Companies worldwide use EDEM to optimize equipment design, increase productivity, reduce operational costs, shorten product development cycles and drive product innovation.
Altair EDEM 2023release is packed with amazing new capabilities and improvements. Central to this release is the ability to use different DEM particle shapes methods, including polyhedron, multi-spheres and sphero-cylinders, within the same simulation. This allows us to considerably expand the range and complexity of applications possible with our market-leading solution. Among the many new features included, we have new physics in the form of a more efficient and shape-agnostic bond model and extended analysis capability with a new residence time for user-defined regions. And, an enhanced API for custom models brings a more integrated experience, including a new GUI preference interface and data stored internally.
What’s New in Altair EDEM 2023 – Release Highlights
Altairis a global technology company that provides software and cloud solutions in the areas of product development, high performance computing (HPC) and data analytics. Altair enables organizations across broad industry segments to compete more effectively in a connected world while creating a more sustainable future.

peeplink.in/3a758fc3a606
NitroFlare
zhhve.setup.rar
Uploadgig
zhhve.setup.rar
Fikper
zhhve.setup.rar.html










Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.